Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is about fundamentally rethinking how an organization operates to make significant improvements in efficiency, productivity, and service delivery. Instead of small, incremental changes, BPR focuses on reimagining entire workflows to address inefficiencies and drive impactful transformation.
What is Business Process Reengineering?
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) involves radically redesigning an organization’s processes to achieve significant improvements in key performance metrics such as efficiency, quality, service, and speed. It goes beyond traditional methods of gradual improvements, demanding a complete rethinking of workflows to align them more closely with strategic business objectives. By fundamentally reshaping processes, BPR enables organizations to eliminate waste, enhance efficiency, and boost customer satisfaction, making them more adaptable and responsive to changes in the business environment.
Key objectives of BPR include:
- Eliminating redundant tasks or bottlenecks that slow down service delivery.
- Leveraging new technologies to automate repetitive or low-value activities.
- Focusing on customer outcomes, ensuring that all processes are aligned with delivering maximum value to clients.
The Key Principles of Business Process Reengineering
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is built on key principles aimed at achieving substantial and sustainable business improvements. For professional service firms, applying these principles can streamline workflows, improve service delivery, and increase efficiency. Below are the main principles that support successful BPR initiatives:
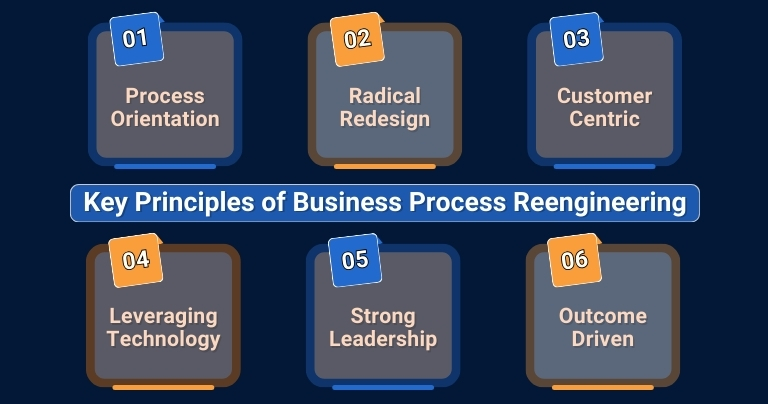
1. Process Orientation
BPR emphasizes optimizing entire processes rather than individual tasks. By taking a holistic view, businesses identify inefficiencies, eliminate bottlenecks, and reduce redundancies, leading to improved performance and client satisfaction. For many companies, integrating Standard Operating Procedures helps to standardize these processes, ensuring consistency and facilitating smoother transitions when changes are implemented.
2. Radical Redesign Instead of Incremental Changes
BPR involves rethinking processes from the ground up rather than making small, incremental improvements. This radical approach allows organizations to break free from outdated systems and make transformative changes that significantly improve operational efficiency and client service.
3. Customer-Centric Redesign
The focus of BPR is to redesign processes with client value in mind. By centering on the client’s needs, businesses can create services that are more responsive, efficient, and customized, which ultimately enhances client satisfaction and loyalty.
4. Leveraging Technology as a Catalyst
Leveraging Technology as a Catalyst: Modern technologies, such as automation and AI, play an important role in facilitating BPR. These tools eliminate inefficiencies, reduce human error, and improve decision-making, streamlining operations and improving agility. Utilizing ERP for Professional Services during the reengineering phase can further help to integrate business functions and improve visibility across projects, making resource management more effective.
5. Strong Leadership and Executive Alignment
Based on the analysis, new processes are designed to improve efficiency and effectiveness. This includes removing redundant steps, integrating new technologies, and aligning workflows with strategic goals. ERP Selection Consultants can assist organizations in choosing the right ERP system that aligns with the newly reengineered processes, providing better support for business operation.
6. Outcome-Driven Focus
Rather than concentrating on individual tasks, BPR emphasizes achieving key outcomes, such as faster project completion or improved customer satisfaction. This outcome-driven focus helps service firms align their processes with their overall business and client goals.
How BPR Differs from Business Process Improvement (BPI)
To differentiate BPR from BPI, let’s first understand Business Process Improvement (BPI).
What is Business Process Improvement (BPI)?
| Aspect | Business Process Reengineering (BPR) | Business Process Improvement (BPI) |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Radical redesign of processes from the ground up. | Incremental changes to refine and improve existing processes. |
| Scope | Focuses on transforming entire workflows and systems. | Focuses on specific areas for gradual improvement. |
| Change Level | High disruption but offers significant long-term improvements. | Low disruption, suitable for continuous, small-scale changes. |
| Objective | Dramatic improvements in cost, quality, service, and speed. | Steady, ongoing improvements in efficiency and accuracy. |
| Use Case | Ideal for businesses needing transformation due to inefficiencies or outdated processes. | Suitable for businesses looking to refine processes that are already functional. |
| Risk and Reward | Higher risk due to the magnitude of changes but offers higher rewards. | Lower risk with more gradual, incremental improvements. |
Choosing Between BPR and BPI
The decision between BPR and BPI depends on the current state of your processes and your business goals. If your processes are functional but need gradual refinement, Business Process Improvement offers an efficient and low-risk solution. However, when facing significant inefficiencies or the need for radical transformation, Business Process Reengineering provides a comprehensive, high-impact approach.
For professional service businesses like those serviced by Haile Solutions, BPR has been a transformative force. Haile Solutions specializes in helping firms re-engineer their core processes to increase charge ability, eliminate inefficiencies, and successfully manage change. Their expert consulting services support businesses in adopting both BPR and incremental business process improvements customized to meet their unique needs.
The BPR Methodology
Implementing Business Process Reengineering (BPR) requires a systematic approach to effectively transform workflows. For professional service firms, following these steps ensures alignment with both client expectations and internal goals:
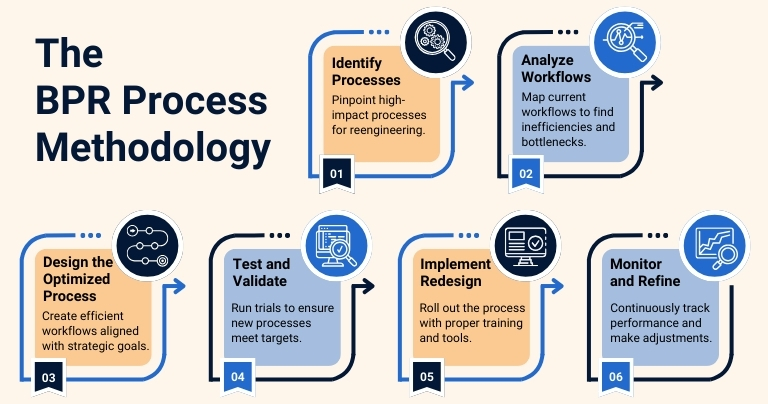
1. Identify Processes for Reengineering
Identify Processes for Reengineering: The first step is identifying processes that need reengineering, typically those affecting client service, resource efficiency, or internal coordination. Focusing on high-impact processes helps maximize improvement efforts.
2. Analyze Current Workflows
Understanding how existing processes function is essential. By mapping out workflows in detail, organizations can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas that need improvement. Conducting a thorough business process assessment at this stage is significant for capturing a complete picture of the current state, allowing targeted changes to be more effective.
3. Design the Optimized Process
Based on analysis, design new processes to improve efficiency and effectiveness by removing redundant steps, integrating new technologies, and aligning workflows with strategic goals. Emphasis is on improving productivity and delivering greater client value.
4. Test and Validate the New Process
Before full implementation, it is better to test the redesigned processes to ensure they meet the desired goals. Pilot programs or controlled trials can help identify areas for further refinement before the changes are implemented across the organization. Firms should also consider the ERP Implementation Cost during this phase to ensure the chosen system meets budget requirements without compromising on necessary functionalities.
5. Implement the Redesigned Process
Rolling out the new processes involves organization-wide adoption, supported by proper training and communication. A well-managed software implementation process is also important to ensure that any new tools or systems introduced align seamlessly with the re-engineered workflows, ensuring a smooth transition for all stakeholders.
6. Monitor and Refine
Continuous monitoring and feedback are essential to ensure the newly implemented processes continue to meet performance targets. Regular data analysis helps identify further improvements, enabling the process to evolve and remain aligned with business objectives.
Benefits of Business Process Reengineering
Business Process Reengineering provides numerous advantages for professional service businesses, particularly in improving operational efficiency and client satisfaction.
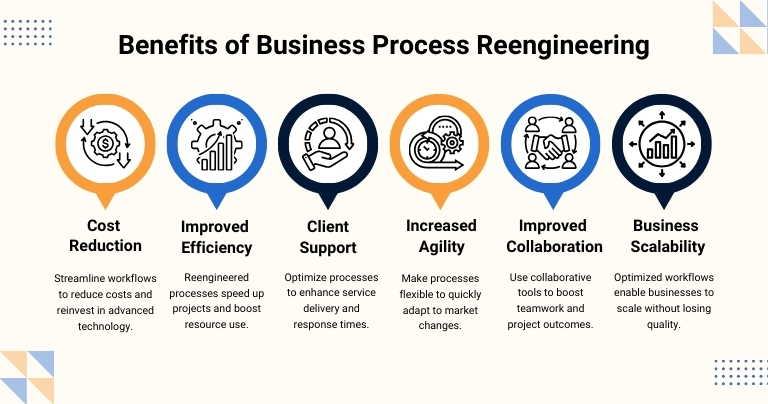
1. Cost Reduction
By streamlining workflows and removing redundant tasks, BPR reduces operational costs, which is particularly beneficial for professional service firms with high labor costs. These savings can be reinvested in technology or client-facing services.
2. Improved Efficiency
Reengineering processes lead to faster project execution and better use of resources. Employees can focus on value-adding activities rather than being bogged down by manual tasks, enabling the firm to deliver services more quickly and efficiently.
3. Better Customer Service
When processes are optimized, businesses can respond to client needs more effectively. By reducing response times and improving service delivery, businesses can provide a more personalized, timely, and higher-quality service experience for their clients.
4. Increased Agility
BPR enables businesses to adapt to market changes and evolving client needs by making processes more flexible. This allows firms to pivot quickly in response to new technologies, regulations, or customer demands, ensuring they remain competitive.
5. Improved Collaboration
BPR often involves the integration of collaborative tools and platforms, such as shared digital workspaces, which specifically encourage teamwork and communication across departments. These tools streamline collaboration, allowing for more effective resource sharing and better project outcomes.
6. Scalability
With optimized processes, businesses are better prepared to scale their operations. Whether taking on more clients or expanding service offerings, streamlined workflows allow companies to handle larger workloads without sacrificing service quality. Leveraging ERP for Small Businesses can also support growing firms by providing an affordable yet effective solution to manage increased demands.
Challenges of Business Process Reengineering
Implementing BPR can present challenges, especially for professional service businesses that rely heavily on established workflows and client relationships.
1. Resistance to Change
Employees may resist workflow changes, especially if they have used the same methods for years. This resistance can delay implementation and reduce the impact of BPR efforts. Addressing this challenge requires effective change management, including clear communication and training.
2. High Initial Costs
BPR requires significant upfront investments in technology, process analysis, and employee training. Although the long-term benefits outweigh these costs, firms must manage expenses carefully to avoid financial strain during the transition.
3. Difficulty in Process Analysis
Mapping complex workflows can be challenging, especially when they rely on individual expertise and personalized client interactions. A thorough analysis is crucial to ensure reengineered processes meet operational needs and client expectations. Leveraging ERP for Professional Services can make this analysis easier by providing tools that track project timelines, client interactions, and resource allocation.
4. Need for Strong Leadership and Vision
Without strong, clear direction, BPR initiatives can lose momentum and face resistance. Leaders must provide strategic guidance, clearly communicate the reasons behind changes, and align teams with the broader goals of transformation.
5. Cultural Shifts
Implementing new processes often requires a shift in organizational culture. In professional service firms, where established practices may be deeply rooted, changing the mindset of employees can be challenging. Leadership must emphasize the benefits of the new processes and create an environment that encourages adaptability.
Haile Solutions specializes in supporting professional service firms through the BPR process by providing expert consulting that ensures success from business process assessment to change management. We help organizations manage the complexities of business process change while increasing chargeability, billability, and client satisfaction. Improved chargeability ensures every hour worked directly contributes to profitability, which is essential for long-term growth.
Role of Technology in BPR
Technology is a powerful enabler of BPR, offering tools that help professional service firms streamline operations, improve efficiency, and deliver better client services.
1. Automation Tools
Automation minimizes manual intervention in repetitive tasks, freeing employees to focus on strategic or creative work. In professional services, this could include automating client invoicing or data entry, allowing staff to focus on client-facing activities.
2. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
ERP systems consolidate business functions, such as billing, resource management, and project tracking, into a single platform. This improves transparency and control, helping firms manage resources and improve service delivery.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI can help businesses analyze data more efficiently, identify trends and provide actionable insights. For professional service firms, AI might assist in optimizing client management or predicting future resource needs based on project data.
4. Cloud Computing and Collaboration Platforms
Cloud-based collaboration platforms allow teams to work together seamlessly, regardless of location. This is particularly important for professional service firms with remote or geographically distributed teams, enabling real-time updates and secure sharing of client data.
5. Data Analytics and Big Data
Data analytics tools help businesses gather insights from large datasets, supporting informed decision-making. Professional service firms can use data analytics to optimize project management, resource allocation, and client communication.
Best Practices for Implementing Business Process Reengineering
Successfully implementing BPR requires more than just redesigning processes—it demands careful planning, strong leadership, and a focus on the end goals. For professional service businesses, adhering to these best practices can help ensure that the transformation delivers tangible results without causing undue disruption to operations.
1. Secure Executive Support
BPR requires top-level support to succeed. Leadership buy-in ensures alignment with broader goals and proper resource allocation. Executives must actively champion the BPR process and communicate its importance to the entire team.
2. Focus on Customer Needs
One of the primary objectives of BPR is to create more customer-centric processes. Professional service firms must ensure that every redesigned process is customized to improve the client experience. This involves gathering client feedback, understanding pain points, and designing workflows that lead to better service delivery.
3. Communicate Changes Clearly
Clear and ongoing communication is vital for ensuring that employees understand the goals of BPR and are fully on board with the changes. Professional service businesses often face resistance to change due to the personalized nature of their work. It’s important to communicate the benefits of the reengineering initiative and how it will improve both operational efficiency and client satisfaction.
4. Use Data-Driven Decision-Making
Successful BPR relies on making data-driven decisions throughout the reengineering process. By leveraging data analytics, professional service businesses can ensure that the redesigned processes are based on real-world insights and are positioned to deliver measurable improvements.
5. Monitor Results and Adjust
BPR is not a one-time project; it’s an ongoing effort that requires continuous monitoring and refinement. After implementing the new processes, it’s important to track key performance indicators (KPIs) to ensure the changes are delivering the desired outcomes. Adjustments should be made as needed to further optimize workflows.
6. Incorporate Change Management
A formal change management strategy is essential to the success of BPR. Change management helps mitigate resistance and ensures that employees understand and embrace the new processes. For professional service businesses, where relationships and established workflows are deeply ingrained, change management is key to minimizing disruptions.
When Should a Business Consider BPR?
Knowing when to adopt Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is important for businesses looking to make significant improvements in efficiency, customer service, and profitability. For professional service businesses, the following scenarios often indicate that BPR could be the right solution:
1. Failing Business Performance
Declining performance metrics such as profitability, revenue growth, or operational efficiency signal that existing processes are no longer effective. When traditional improvement methods fail, BPR offers a way to redesign core processes to restore and improve business performance.
2. Outdated Processes
As industries evolve, businesses may rely on outdated processes that slow down operations and reduce competitiveness. BPR enables organizations to replace legacy workflows with modern, more efficient systems, ensuring they remain agile and responsive to market demands.
3. Customer Dissatisfaction
Rising client complaints or declining satisfaction are indicators that significant processes such as client communication or service delivery—need reengineering. BPR helps improve the customer experience by aligning processes more closely with client needs and expectations.
4. Rising Operational Costs
Escalating costs without a corresponding increase in revenue often indicate inefficiencies within core processes. BPR helps businesses streamline workflows, reduce costs, and improve operational effectiveness.
5. Inability to Compete in the Market
Businesses that struggle to keep up with market trends or competitors may benefit from BPR. Redesigning processes to align with current market needs and technological advancements allows businesses to regain their competitive edge.
Case Studies: Successful BPR Implementations
Real-world examples of Business Process Reengineering provide valuable insights into how organizations across different professional service industries have successfully re-engineered their workflows, leading to significant operational improvements and improved service delivery. Below are diverse examples from different professional service sectors.
1. CPA - Accounting Firm: Reengineering the Client Billing Process
We worked with a CPA firm with a growing client base that was struggling with delays in client billing due to inefficient manual invoicing processes. The firm faced challenges managing multiple accounts, resulting in delayed payments and missed billing cycles.
BPR Initiative: The firm implemented BPR to transition from manual billing to an automated ERP integrated with existing accounting systems.
Results: The firm reduced its billing cycle by over 50%, leading to faster payments, reduced DSO (days sales outstanding), improved cash flow, and fewer invoice errors. This strengthened the firm’s ability to handle more clients without additional resources.
2. Advertising Agency: Redesigning Project Management
A large ad agency was facing difficulties in coordinating multiple projects simultaneously, leading to miscommunication between design teams, delays in project delivery, and frustrated clients.
BPR Initiative: The firm reengineered its project management workflow by adopting a centralized project management system. The new system enabled real-time updates, improved collaboration between teams, and better resource allocation.
Results: The agency achieved a 30% improvement in project completion times, reduced communication errors, and improved client satisfaction. This had significant improvements in the agency’s margins.
3. Legal Services: Optimizing Case Management
A legal services firm was experiencing inefficiencies in handling multiple client cases due to a disjointed case management system. Each department operated independently, leading to delays in case preparation and client communication.
BPR Initiative: The firm used BPR to integrate its case management system, enabling seamless communication and streamlined document sharing across departments.
Results: The integrated system led to a 40% reduction in case preparation time, allowing the firm to handle more clients while improving the overall client experience.
4. IT Consulting Firm: Reengineering Knowledge Management
An IT consulting firm faced difficulties in managing the large volume of client information and knowledge accumulated from various projects. The decentralized storage system made it difficult for consultants to access relevant project data efficiently.
BPR Initiative: The firm reengineered its knowledge management system, centralizing all project documentation and client data into a cloud-based knowledge hub, enabling consultants to access information quickly and collaborate more effectively.
Results: The firm reduced time spent searching for client information by 60%, improving consultant productivity and allowing faster project execution for clients.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is Business Process Reengineering only for large organizations?
No, BPR can be implemented by businesses of all sizes. While large organizations often have more complex workflows that may require extensive reengineering, small and medium-sized businesses can also benefit from BPR by streamlining their operations and becoming more agile.
2. How long does it typically take to implement BPR?
The duration of a BPR project can vary widely depending on the complexity of the processes being reengineered and the size of the organization. On average, a BPR project can take several months to over a year. Factors such as the depth of analysis, employee training, and technology integration can also affect the timeline.
3. What are the risks involved in Business Process Reengineering?
BPR carries certain risks, including resistance to change from employees, high initial costs for technology and training, and potential disruptions to daily operations during implementation. These risks can be mitigated with strong leadership, clear communication, and effective change management practices.
4. Can BPR be used in conjunction with other process improvement methods?
Yes, BPR can complement other methodologies like Lean or Six Sigma. While BPR focuses on radical transformation, Lean and Six Sigma emphasize continuous, incremental improvements. Some organizations use BPR to address major inefficiencies and then adopt Lean or Six Sigma for ongoing process optimization.
5. What is the role of employees in the BPR process?
Employees play a significant role in the success of BPR. Their involvement in providing insights into current workflows, identifying inefficiencies, and offering feedback on proposed changes is essential. Additionally, employee involvement and training are essential for ensuring a smooth transition to new processes and overcoming resistance to change.





