What is Business Process Documentation?
Business process documentation refers to the act of capturing, detailing, and maintaining the steps, tasks, and activities that make up a business process. Essentially, it is a written record that describes how a particular business process is executed, including who is responsible, what resources are involved, and what the expected outcomes are.
This documentation can take various forms, such as flowcharts, diagrams, step-by-step guides, or detailed manuals. The purpose is to create a clear, accessible, and organized reference that anyone within the organization can use to consistently understand and execute the process.
Importance of business process documentation
- Improved Efficiency: Clear, standardized processes eliminate ambiguity and reduce rework, leading to faster project completion and significant cost savings.
- Strengthened Consistency: Uniform execution across teams and projects ensures a culture of standardization and quality.
- Streamlined Training: New employees can quickly become familiar with comprehensive process documentation, reducing training time and costs.
- Simplified Communication: Sharing documentation with clients, partners, and stakeholders promotes transparency and collaboration.
- Identify Areas for Improvement: Analysing processes helps pinpoint inefficiencies and areas for enhancement. Haile Solutions’ process improvement services can help businesses analyze these gaps & further improve them.
- Standardize Operations: Eliminate redundant tasks for a more focused workflow.
- Improve Team Collaboration: Facilitate better communication and coordination within teams.
- Audit and Compliance Readiness: Be prepared for audits and regulatory compliance with well-documented processes.
Industry Relevance of Business Process Documentation
Business process documentation is essential across various industries, serving as a foundational tool that drives efficiency, compliance, and continuous improvement. Here’s how it plays a significant role in different sectors:
Architecture and Design Firms
In architecture, documentation ensures adherence to design processes, client requirements, and regulatory compliance. It facilitates collaboration among architects, engineers, and contractors, providing clear guidelines on project specifications and reducing errors and delays.
Accounting Firms (CPA)
Business process documentation ensures accuracy and consistency in financial reporting, auditing, and tax preparation. It helps maintain compliance with accounting standards and regulations, and facilitates training and knowledge transfer among accountants.
Consultancies
Consulting firms rely on process documentation to standardize methodologies and ensure consistent service delivery. It supports knowledge management, enabling consultants to apply best practices and past project experiences, thereby enhancing the firm’s value proposition to clients.
Public Relations (PR)
In PR, documentation supports the management of communication strategies, media relations, and crisis management protocols. It ensures that PR campaigns are executed consistently, with clear guidelines on messaging, client approvals, and media outreach.
Market Research Companies
Documentation in market research ensures the integrity and consistency of research methodologies, data collection, and analysis. It maintains the credibility of research findings, ensures compliance with industry standards, and facilitates efficient project management.
Law Firms
Law firms rely on process documentation to manage case files, client communications, and compliance with legal standards. It standardizes legal processes, ensuring that services are delivered consistently and in compliance with ethical and professional standards.
Financial Services
Documentation ensures compliance with regulations like AML and data protection laws, supporting internal audits and risk management, and reducing the risk of financial discrepancies.
IT and Software Development
Documentation in IT maintains consistent coding standards and processes, ensuring knowledge transfer and continuity, particularly in agile environments where roles frequently change.
Public Sector and Government
Documentation supports transparency, accountability, and efficiency, ensuring that government services are delivered consistently and in compliance with legal requirements.
Education
Educational institutions use documentation to standardize administrative processes, ensuring consistency, fairness, and efficiency, and to meet accreditation requirements.
Healthcare Industry
In healthcare, documentation is important for compliance with strict regulations, patient care protocols, and safety standards. It also facilitates staff training, ensuring high-quality care and safety.
Types of Business Process Documentations
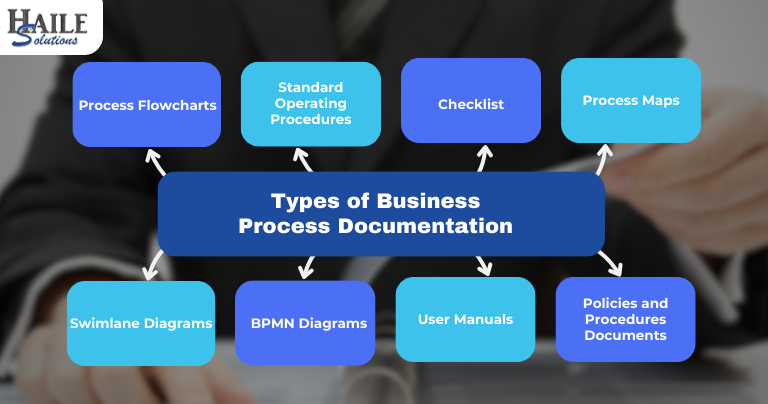
| Type of Documentation | Description | Use Case |
| Process Flowcharts | Visual diagrams that map out steps in a process using symbols and arrows. | Useful for visual learners and processes with multiple decision points or branches. |
| Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) | Detailed, written instructions outlining how to perform specific tasks or operations. | Ideal for industries where consistency and compliance are essential such as audit, due diligence, manufacturing, and healthcare. |
| Checklists | Simple lists of tasks to be completed in a specific order. | Perfect for routine processes or tasks that require thoroughness, like safety inspections and quality control. |
| Process Maps | Detailed visual representations of a process, including responsible parties, resources, and timelines. | Useful for complex processes involving multiple teams or systems, helping to identify inefficiencies. |
| Swimlane Diagrams | Cross-functional flowcharts that divide a process into lanes, showing responsibility by department or individual. | Helpful for processes involving multiple stakeholders, clarifying task ownership and handoffs. |
| BPMN Diagrams (Business Process Model and Notation) | Standardized method that uses specific symbols to create detailed models of processes. | Best suited for detailed, complex processes, especially in industries like finance and IT. |
| User Manuals | Comprehensive documents provide instructions on using a system, tool, or product. | Essential for training, onboarding, and supporting users in effectively operating systems or products. |
| Policies and Procedures Documents | Broader guidelines outlining how processes should be carried out within an organization. | Vital for ensuring employees understand the rules and regulations governing their work. |
Key Components of Business Process Documentation
Creating effective business process documentation involves several key components. These components ensure that the documentation is clear, comprehensive, and useful for everyone in the organization. Here’s a breakdown of the essential elements that should be included:
1. Process Title
The process title is the first thing users will see. It should clearly and concisely describe the process being documented. The title helps users quickly identify what the document covers and whether it’s relevant to their needs. This is the best way to document business processes effectively.
Example: “Customer Onboarding Process” or “Invoice Approval Procedure”
2. Purpose
The purpose section explains the process’s existence and its aims. It provides context for the process and helps users understand its importance within the organization.
Example: “The purpose of this process is to ensure that all new customers are properly onboarded, leading to a smooth start and long-term satisfaction.”
3. Scope
The scope outlines what is included in the process and what is not. It defines the process’s boundaries, helping users understand the specific areas it covers.
Example: “This process applies to all new customers in the North American region and excludes existing customers who are upgrading their services.”
4. Roles and Responsibilities
This component lists the people or departments involved in the process and their specific roles. It clarifies who is responsible for each step, ensuring accountability and smooth handoffs between tasks.
Example: “The Sales Team is responsible for initial customer contact, while the Onboarding Team handles account setup and training.”
5. Step-by-Step Instructions
The heart of the documentation, this section provides detailed, step-by-step instructions for carrying out the process. Each step should be clear and easy to follow, using simple language. Diagrams or flowcharts can be included to visually represent the steps.
Example:
- Step 1: Sales Team contacts the new customer to schedule an onboarding meeting.
- Step 2: Onboarding Team sends a welcome email with account setup instructions.
- Step 3: Customer completes account setup and confirms with the Onboarding Team.
6. Tools and Resources
This section lists any tools, software, or resources needed to complete the process. It ensures that users have everything they need to follow the process effectively.
Example: “This process requires access to the CRM system, email templates, and the onboarding checklist.”
7. Process Flow Diagrams
Diagrams or flowcharts can visually represent the process, making understanding the flow of activities easier. These visual aids are especially helpful for complex processes with multiple steps or decision points, such as when creating a process definition document.
Example: A flowchart showing the steps from initial customer contact to account setup completion.
8. Compliance and Regulations
This section should outline any legal or regulatory requirements the process is subject to. It ensures the process complies with all necessary standards and helps the organization avoid legal issues.
Example: “This process must comply with GDPR for data protection and customer privacy.”
9. Review and Approval
Documentation should include information about who reviewed and approved the process. This adds credibility and ensures that the appropriate parties have vetted the process.
Example: “This process was reviewed by the Compliance Officer and approved by the Head of Operations on [Date].”
10. Revision History
The revision history tracks any changes made to the process over time. It helps users understand the evolution of the process and ensures they are using the most up-to-date version.
Example:
- Version 1.0: Initial document created on [Date].
- Version 1.1: Updated steps for account setup on [Date].
Steps to Effective Business Process Documentation
Haile Solutions can expertly guide businesses through each step of the process documentation, ensuring that every aspect is customized to meet the organization’s specific needs and goals:
| Step | Description | Example |
| 1. Identify the Process to Document | Choose and prioritize processes essential to business operations, particularly those that are complex or prone to errors. | Documenting the client onboarding process in a consulting firm. |
| 2. Gather Necessary Information | Collect relevant details by interviewing stakeholders and reviewing existing documentation. | Interview account managers, legal and IT teams involved in onboarding. |
| 3. Define the Process Scope | Clearly define what is included in the process and set boundaries to maintain focus and relevance. | Onboarding starts with the client’s agreement and ends after the first service delivery. |
| 4. Break Down the Process into Steps | Divide the process into clear, actionable steps detailing responsibilities and required resources. | Step 1: Finalize client agreements. Step 2: Set up client access. Step 3: Schedule a kick-off meeting. |
| 5. Create Visual Aids | Use flowcharts or diagrams to visually represent the process, making it easier to understand. | A flowchart showing the client onboarding process from agreement to service delivery. |
| 6. Assign Roles and Responsibilities | Clearly define responsibilities for each step to ensure accountability. | Account managers handle client communication; IT manages system setup. |
| 7. Review for Accuracy and Completeness | Have stakeholders review the documentation to ensure accuracy and completeness. | Account managers, legal, and IT teams review the onboarding documentation for accuracy. |
| 8. Test the Documentation | Test the documentation with someone new to the process to identify gaps or unclear instructions. | A new account manager follows the documentation to onboard a client and provides feedback. |
| 9. Update and Maintain the Documentation | Regularly review and update the documentation to keep it current as processes evolve. | Review the client onboarding documentation every six months for updates. |
| 10. Distribute and Train | Share the finalized documentation with relevant parties and provide necessary training. | Distribute to account managers & IT and conduct a training session to ensure everyone is aligned. |
Tools and Software for Business Process Documentation
Advanced Software Solutions
Advanced business process documentation tools offer powerful features beyond simple documentation. Software like ARIS and IBM Blueworks Live provides comprehensive process modeling, real-time collaboration, and integration with other business systems. These tools allow businesses to create detailed process models, automate workflows and ensure compliance with industry standards. Customization options and the ability to integrate with existing business systems make these tools particularly valuable for large organizations with complex processes.
Choosing the Right Tool
Selecting the right tool for business process documentation depends on your specific needs. Consider factors such as ease of use, collaboration features, integration capabilities, and cost. For instance, smaller businesses benefit from more straightforward tools like Lucidchart or Trello, while larger enterprises may require the advanced features of Bizagi Modeler or Microsoft Visio. Conducting a cost-benefit analysis can help determine the best tool for your organization, balancing functionality with budget constraints.
Case Studies On Business Process Documentation
Case Study 1: Rapidly growing Advertising Agency
- Challenge: A rapidly growing ad agency lacked standard processes or documentation. The team was busy delivering creative work for their clients.
- Solution: The Agency Implemented a standardized template and structure for documenting all processes. It also used a centralized system to store and manage documents, ensuring everyone had access to the latest versions.
- Outcome: Improved consistency in process documentation, making it easier for team members to follow and understand. This led to more efficient training, onboarding, and smoother transitions during role changes.
- Lessons Learned: Without a standardized approach, documentation can become fragmented and complex to follow, leading to errors and miscommunication. Ensuring buy-in from all team members is critical for success.
- Best Practices: Review and update documentation regularly to reflect any process changes. Encourage team collaboration during documentation to capture diverse perspectives and improve accuracy.
Case Study 2: Small Consultancy
- Challenge: A small consultancy lacked standard documents and templates, meaning that every project was bespoke, and they had to create all the documentation from scratch.
- Solution: We helped them develop a set of standard documents and templates for common project tasks and phases. The team customizes these templates for each project but maintains a consistent structure to streamline the process.
- Outcome: The consultancy reduced the time spent creating documents from scratch, leading to faster project setup and increased efficiency. With a more consistent approach, the quality of deliverables improved, and the team could focus more on client-specific needs rather than administrative tasks.
- Lessons Learned: Starting from scratch for each project is time-consuming and reduces efficiency. Standardized templates allow the team to work more effectively and ensure consistency across projects.
- Best Practices: Regularly update and refine templates based on feedback and evolving project requirements. Train the team on using and adapting the templates effectively to maintain quality and efficiency.
Case Study 3: Medium-sized CPA firm
- Challenge: A medium-sized CPA firm is a result of several mergers & acquisitions of smaller firms. Each office had different processes so:
- Opportunities to gain economies of scale were lost
- Staff struggled when moving between offices or interoffice teams
- Best practices were not followed
- Solution: Conducted a comprehensive review of all processes across the merged offices and created a unified set of standard operating procedures (SOPs). They implemented training programs to ensure all staff were familiar with the new standardized processes and established a process governance team to monitor adherence.
- Outcome: The CPA firm realized significant efficiency gains by aligning processes across offices, enabling better resource sharing and operational consistency. Staff mobility between offices improved, and best practices were more consistently applied, enhancing service quality and client satisfaction.
- Lessons Learned: Inconsistent processes can hinder growth and operational efficiency, especially in firms formed through mergers. Standardization is key to realizing economies of scale and ensuring smooth operations across multiple locations.
- Best Practices: Involve representatives from all offices in the process standardization efforts to ensure buy-in and address specific needs. Regularly review and update the SOPs to reflect changes in regulations or business practices and maintain ongoing training to reinforce the standard processes. Establish metrics to monitor compliance and continuously improve the processes.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Documenting business processes is essential, but it’s not without its challenges. Understanding these common obstacles and how to overcome them can help ensure your documentation efforts are successful and sustainable.
1. Lack of Stakeholder Buy-In
Challenge:
One of the most common challenges is getting buy-in from stakeholders. Without their support, documentation efforts may be viewed as low priority, leading to incomplete or outdated documentation.
Solution:
To overcome this, emphasize the benefits of documentation, such as improved efficiency, compliance, and training. Involve stakeholders early in the process to gather their input and make them feel invested in the outcome. Highlighting how documenting as is business processes can make their jobs easier and contribute to the organization’s success can also help gain their support.
2. Complexity of Processes
Challenge:
Some business processes are inherently complex, making them difficult to document accurately and comprehensively. This complexity can lead to confusion or errors in the documentation.
Solution:
Break down complex processes into smaller, more manageable parts. Use visual aids like flow charts or diagrams to simplify understanding. Consult with subject matter experts to ensure that all process aspects are accurately captured. Regular reviews and updates can also help refine and clarify complex documentation, providing clear process document examples.
3. Keeping Documentation Up-to-Date
Challenge:
Processes change over time, and keeping documentation current can be challenging. Outdated documentation can lead to consistency and errors.
Solution:
Establish a regular review schedule to update documentation. Assign responsibility for documentation maintenance to specific individuals or teams. Encourage a culture of continuous improvement where employees are encouraged to report changes in processes, ensuring that documentation reflects the latest practices.
4. Lack of Standardization
Challenge:
Consistent documentation formats or styles can create confusion and make it easier for employees to follow or locate the necessary information.
Solution:
Implement a standardized template or format for all process documentation. This will ensure consistency and make the documentation easier to read and understand. Provide training on how to use the standardized templates and enforce adherence to these standards across the organization.
5. Insufficient Resources
Challenge:
Creating and maintaining business process documentation can be resource-intensive, requiring time, tools, and expertise that may be in short supply.
Solution:
First, prioritize the most vital documentation processes. Use tools and software that streamline the documentation process, such as templates, automation, or process mapping software. Where possible, allocate dedicated resources or teams for documentation tasks and consider training more employees to contribute to the process.
6. Employee Resistance
Challenge:
Employees might resist process documentation efforts, viewing them as extra work or unnecessary bureaucracy.
Solution:
Address this resistance by explaining how documentation can reduce confusion, improve efficiency, and make their jobs easier. Involve employees in the documentation process so they feel a sense of ownership. Show quick wins by demonstrating how documented processes have already led to positive organizational outcomes.
With the specialized guidance of Haile Solutions, companies can tackle these challenges head-on, ensuring their process documentation is effective and resilient to business-specific complexities.
Future Trends in Business Process Documentation
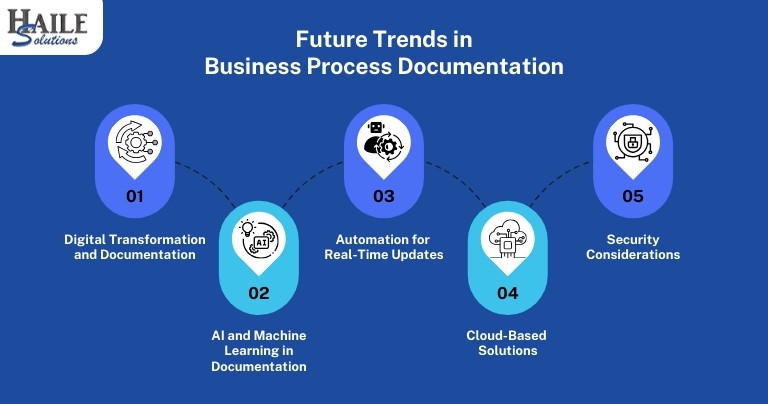
Digital Transformation and Documentation
Digital transformation streamlines business process documentation, making it more integrated and accessible. Digital tools enable the creation of dynamic, real-time documentation that can be easily updated as processes change.
AI and Machine Learning in Documentation
AI and machine learning are automating business process documentation. These technologies analyze existing processes, suggest improvements, and automatically update documentation, reducing the need for manual maintenance.
Automation for Real-Time Updates
Automation tools keep documentation up to date by automatically capturing and reflecting process changes as they occur. This ensures that documentation remains accurate and reflects the latest practices.
Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based documentation offers easy access, collaboration, and scalability, enabling remote work and cross-departmental cooperation. However, it requires strong security measures, such as encryption and access controls, to protect sensitive information.
Security Considerations
Security is critical for cloud-based documentation. To mitigate risks, organizations should choose providers that comply with regulations, implement strong access controls, and educate employees on cloud security best practices.
Measuring the Impact of Business Process Documentation
Evaluating the effectiveness of business process documentation is essential to ensure it provides real value. Businesses can measure the impact of their documentation efforts by focusing on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and calculating Return on Investment (ROI).
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Identifying KPIs for Measuring Documentation Effectiveness
Key KPIs to track include:
- Process Compliance Rate: Measures how consistently employees follow the documented processes.
- Error Reduction: Tracks the decrease in errors after implementing documentation.
- Training Time: Measures how quickly new employees can be trained using the documentation.
- Process Improvement Frequency: Indicates how often processes are refined based on documented insights.
- Employee Satisfaction: Assesses how helpful employees find the documentation through surveys.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Methods for Calculating ROI from Process Documentation Efforts
To calculate ROI:
1. Quantify Benefits:
- Time Savings: Estimate the time saved through more efficient processes and reduced errors.
- Cost Reduction: Calculate savings from fewer errors and better compliance.
- Productivity Gains: Estimate productivity increases due to better process adherence.
2. Calculate Costs:
- Development Costs: Include the costs of creating and maintaining documentation.
- Maintenance Costs: Consider ongoing update costs.
3. Determine ROI: Use the formula:
ROI = (Total Benefits – Total Costs)/Total Costs × 100
A positive ROI indicates that documentation is delivering value beyond its costs.
Frequently Asked Quetions
1. What tools are used for business process documentation?
Common tools include: –
- Atlassian Jira: Widely used for project management & process documentation
- Zoho Projects: A comprehensive suite with robust documentation features.
- Freshservice: An IT service management platform with strong process documentation capabilities.
Other tools include Microsoft Visio for flowcharts, Lucidchart for real-time collaboration, Trello for task management, and Confluence for creating and sharing detailed documentation.
2. Who is responsible for business process documentation?
Responsibility typically lies with process owners or department heads but it can also involve dedicated documentation teams or cross-functional teams that include subject matter experts.
3. How can business process documentation improve compliance?
Proper documentation ensures that all processes are performed consistently, provides an audit trail, and serves as evidence during audits that the organization adheres to regulatory standards.
4. How often should business process documentation be updated?
Business process documentation should be reviewed and updated regularly, typically every 6 to 12 months or whenever significant changes occur in the process.





